Fire Fighting System
Hydrant system
The design of a fire hydrant system is a critical aspect of fire safety, aimed at providing an efficient, reliable, and accessible water source for firefighting operations. The design must consider factors such as water supply, pressure requirements, flow capacity, and accessibility to ensure the system operates effectively in the event of a fire.
Key Elements of Fire Hydrant System Design:
Water Supply:
A fire hydrant system is typically connected to a municipal water supply or an independent water source, such as a private tank or reservoir. The water supply must have enough capacity to support the demands of firefighting, ensuring adequate flow rates and pressure.
Hydrant Placement:
Hydrants should be strategically placed to provide coverage for the entire area, taking into account factors like building size, layout, and fire hazard classification. Typically, hydrants are spaced at regular intervals (e.g., every 100-150 meters) to ensure no area is too far from a hydrant.
They must also be located in accessible, unobstructed locations for fire trucks and personnel.
Hydrant Type:
Fire hydrants come in various designs, but the most common types include wet barrel (where water is constantly available) and dry barrel (where the water is stored below ground and is released when needed). The choice of hydrant type depends on climate conditions and local regulations.
Piping Network:
The hydrant system’s underground piping must be designed to deliver water efficiently. The system should be sized based on the required flow and pressure to meet firefighting needs. The pipes are generally made of durable materials such as ductile iron or PVC, and they are designed to withstand high-pressure demands during emergencies.
Pressure and Flow Requirements:
Fire hydrants must be designed to deliver a sufficient flow rate (measured in gallons per minute or liters per second) and pressure (measured in psi or bar) to ensure that firefighting efforts are effective. This is determined based on factors such as the type of building or area being protected, local fire codes, and the water supply’s capabilities.
Valves and Controls:
Each hydrant is equipped with a valve mechanism that controls the flow of water. Proper design ensures the valve is easily operable and durable, even in extreme weather conditions. In some cases, additional control valves and pressure-reducing valves may be incorporated to regulate water flow and pressure.
Maintenance and Accessibility:
The design must also account for ease of maintenance, with hydrants located in areas that are easy to inspect and service. Hydrants should be clearly visible and easily identifiable, with markings indicating their location and water flow capacity.
Regular maintenance schedules, inspections, and pressure testing should be built into the design to ensure the system remains functional.
Standards and Regulations:
The design of fire hydrant systems must comply with local fire safety codes, national standards (such as NFPA or British Standards), and building codes. These regulations define the minimum requirements for hydrant spacing, water supply pressure, and system components to ensure public safety.
In conclusion, a well-designed fire hydrant system is integral to a community’s fire protection strategy. The system must be tailored to the specific needs of the area, ensuring that hydrants are strategically located, capable of delivering adequate flow and pressure, and are easy to maintain and operate in emergencies.
Medium Velocity Water Spray System (MVWS)
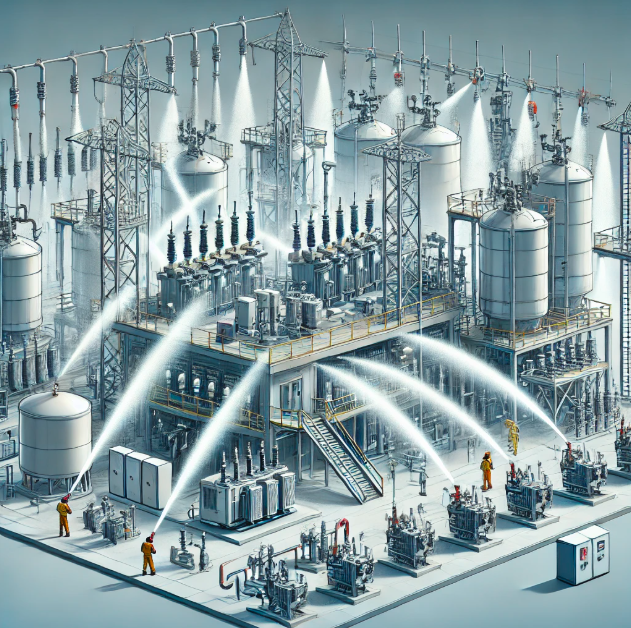
A Medium Velocity Water Spray System (MVWS) is a specialized fire protection system designed for cooling, fire suppression, and exposure protection. It effectively controls radiant heat and prevents fire spread by discharging water through strategically positioned nozzles in a fine spray pattern.
Key Features:
✅ Ideal for protecting oil tanks, transformers, conveyors, and industrial equipment
✅ Provides uniform water distribution to prevent overheating
✅ Reduces fire intensity by cooling surrounding areas
✅ Customizable nozzle arrangements for optimal coverage
Applications:
✔ Power plants & substations
✔ Oil & gas facilities
✔ Chemical processing units
✔ Conveyor belts in industrial setups
Fire Detection System
A Fire Detection System is a crucial safety mechanism designed to detect fire, smoke, or heat at an early stage and trigger alarms for rapid response. These systems help prevent property damage and save lives by providing timely alerts.
Types of Fire Detection Systems:
🔥 Smoke Detectors – Detect smoke particles in the air
🔥 Heat Detectors – Sense a rapid rise in temperature
🔥 Flame Detectors – Identify open flames using infrared or ultraviolet sensors
🔥 Gas Detectors – Detect hazardous gases that may lead to fires
🔥 Automatic Fire Alarm Systems – Integrated systems that trigger alarms and notify emergency responders
Fire Extinguishers
A fire extinguisher is a portable device designed to control or extinguish small fires in emergencies. They are essential safety tools used in homes, offices, industries, and vehicles. Fire extinguishers come in different types, each designed for specific fire hazards.
Types of Fire Extinguishers:
🔥 Water-Based (Class A) – For wood, paper, and fabric fires
🔥 CO₂ (Class B & Electrical) – For flammable liquids and electrical fires
🔥 Dry Powder (Class A, B, C) – For general-purpose fire protection
🔥 Foam (Class A & B) – For flammable liquids and solid fires
🔥 Wet Chemical (Class K/F) – For kitchen fires involving cooking oils
